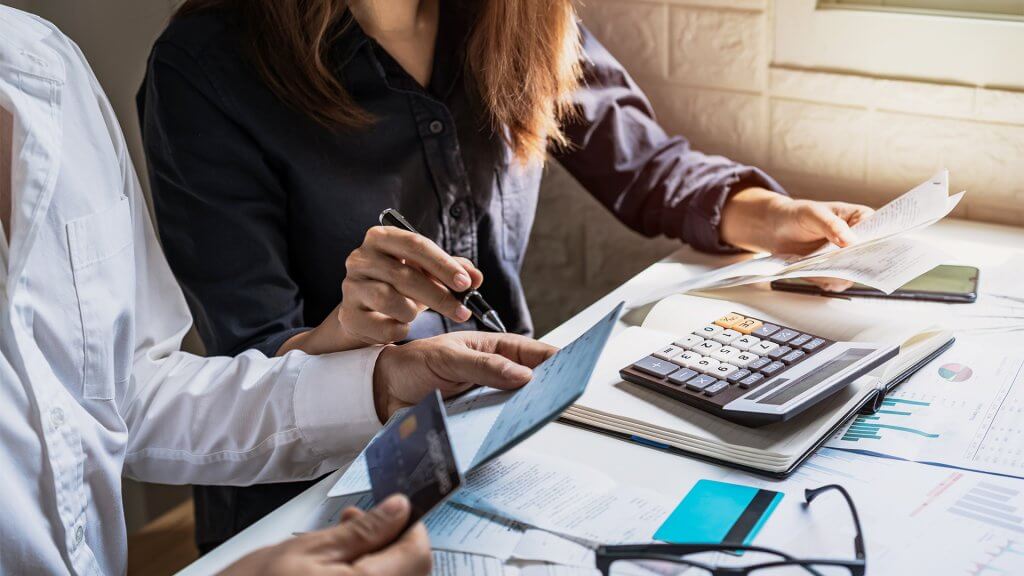
The consequences of climate change extend beyond changes in weather patterns. Its effects also directly affect food safety and security. Extreme weather events disrupt agricultural practices and food production. It also encourages the multiplication of foodborne pathogens. Below are some direct effects of climate change on food safety.
1. Increase in Foodborne Illnesses
Climate issues affect the prevalence of food-related pathogens. Unfortunately, this occurs in several ways. For starters, the continuously rising global temperatures create perfect conditions for the growth and survival of foodborne pathogens.
Warm temperatures increase their reproduction rates, increasing their concentration within food. Similarly, extended periods of warm temperatures lengthen the window for bacterial growth and contamination, increasing the likelihood of these outbreaks.
Temperatures aside, climate change interrupts the normal precipitation patterns. Affected regions may experience excessive rains or droughts, each with negative implications on foodborne pathogens.
High rainfall causes flooding, introducing pathogens from animal waste and contaminated water sources. On the other hand, the concentration increases during drought. Using contaminated water for irrigation transfers these pathogens to crops.
Similarly, climate changes ultimately lead to changes in agricultural practices. Farmers will be forced to adopt different practices, which increases the risks of foodborne illnesses. For instance, they may be forced to rely on organic manure to boost soil fertility. While this is prudent, inadequately treated organic manure harbors pathogens contaminating farm produce.
2. Changes in Food Storage and Preservation
Climate changes also affect food storage. It affects the safety and quality of food products going through the supply chain in the following ways:
- Increase energy demand: High temperatures means there’s demand for refrigeration during storage. Storage facilities should maintain low temperatures to prevent spoilage and bacterial growth. This increases energy consumption in these facilities.
- Effect on cold chain logistics: Climate change also disrupts reliability of cold chain facilities, which are especially important for preserving perishable goods. Temperature fluctuations during transit or storage increases the risk of breaches, compromising the quality of food products.
Due to these issues, relevant individuals need to find ways to enhance food storage. The most obvious is alternative preservation methods, like natural preservatives, which reduce chemical exposure.
Authorities should also develop innovative packaging and testing technologies to enhance safety. Modern technologies like moisture absorbers and oxygen scavengers help maintain freshness and safety of food products during storage. Warehouses can also embrace technologies like food X-ray machines that offer superior contaminant detection for various products
3. Vulnerabilities of Fisheries and Aquaculture
Climate change also threatens fisheries, making the availability of safe seafood products challenging. Warm ocean temperatures have a negative impact on marine ecosystems. For instance, rising water temperatures forces marine species to migrate to cool waters. This changes the distribution and composition of aquatic species. Warm water also promotes the growth of pathogenic bacteria, which contaminates seafood. Similarly, extreme weather events like storms disrupt aquatic operations.
Endnote
Climate change has significant impacts on food safety, so individuals and relevant authorities should take proactive measures to ensure continuous food safety and security. Addressing the risks by improving various practices and tightening regulations can mitigate the impact of climate change on food safety.