Maybe you’ve heard or read the term “phishing” before and have wondered what, exactly, it was referring to. In the below article, we are going to discuss phishing, some of the most common ways cybercriminals attempt to use phishing tactics and how to guard against them.
What is phishing?
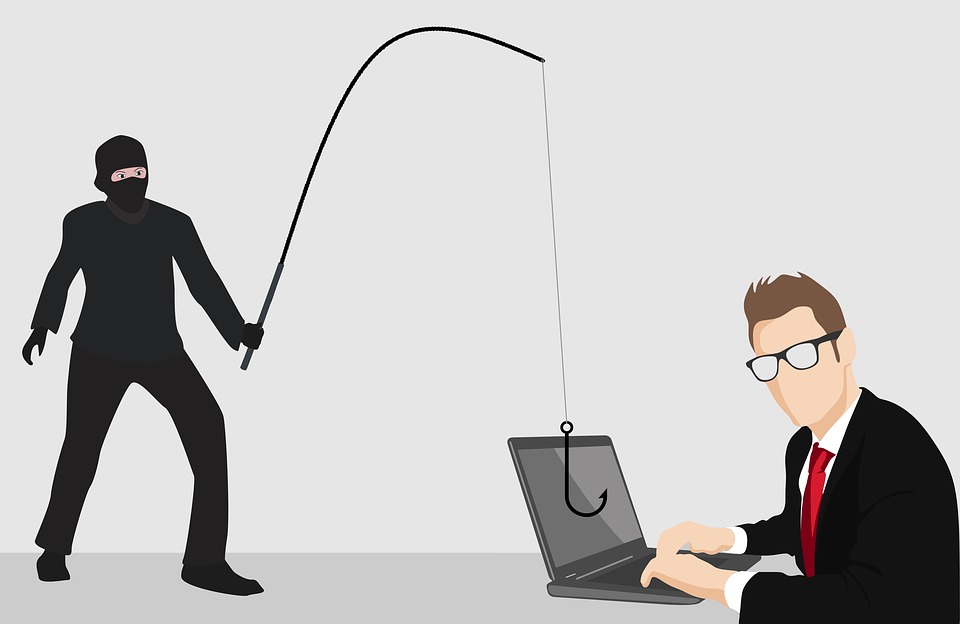
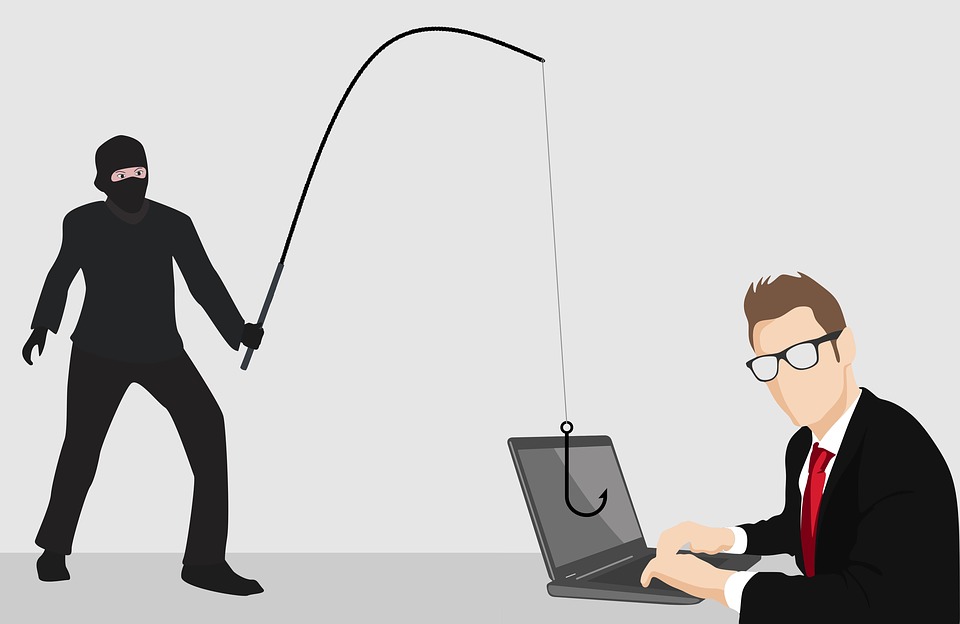
Phishing is a type of online fraud in which criminals impersonate a legitimate business to obtain sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card numbers. It is typically done through email or text messages that contain links to malicious websites or attachments containing malware, but it can also be done through social media and other online channels.
Phishing attacks usually target a wide range of victims and are often very sophisticated, making them difficult to detect. The best defence against phishing, whether you’re an individual or a business, is to remain vigilant and educate yourself about the different types of phishing attacks.
Below are some of the most common ways cybercriminals try to “phish” for sensitive information and gain unauthorised access.
Vishing
Vishing is a form of phishing that uses voice messages sent over the phone, with the goal of obtaining sensitive information. It typically involves a caller pretending to be from a legitimate business or government agency and asking the victim to provide personal information such as passwords or banking details.
To guard yourself against vishing attacks, never give out personal information over the phone and always verify who is calling by asking for contact details.
If you are in doubt, hang up immediately and call the company or agency at a number you know to be legitimate. To play it even safer, there are helpful phone number ID tools that let you see where the number is coming from before you decide to pick up or call back.
Email Phishing
Email phishing is where criminals send emails that appear to be from legitimate sources, such as banks or other financial institutions. The goal is to get users to click on malicious links or open attachments that contain malware or keyloggers.
Often, these emails will include a sense of urgency to increase the likelihood that users will respond. Examples of email phishing messages may include requests for personal information, passwords or security questions and answers.
To guard yourself against email phishing, it’s important to be aware of the tell-tale signs. These include messages that contain spelling and grammar mistakes, have generic salutations (such as “Dear Customer”), or ask for personal information.
It’s also important to never open attachments from suspicious emails and never click on any links contained in them.
Social Media Phishing
Social media phishing is when criminals pose as legitimate companies or individuals on social media platforms, such as Facebook and Twitter. They use these platforms to gain access to personal information and passwords and they are increasingly common.
To protect yourself from social media phishing attacks, be sure to only accept friend requests from people you know, never give out personal information in response to messages or posts and be aware of any suspicious activity on your account.
Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is a more targeted form of phishing attack, in which criminals target specific individuals or organisations. The criminals create a message that appears to come from someone the victim knows or trusts, such as a colleague or acquaintance. The goal is to get the victim to click on a malicious link or open an attachment that contains malware.
Be aware of spear phishing by never clicking on links or opening attachments from unknown sources, and always double-check the email address of the sender before taking any action.
Conclusion
Overall, phishing attacks have become increasingly sophisticated, making it difficult to recognize them. The best defense against phishing is to remain vigilant, educate yourself about the different types of attacks and take precautions to protect yourself. Be aware of the tell-tale signs and never give out personal information or click on suspicious links or attachments. Taking these steps can help you minimise your risk of falling victim to a phishing attack.